🧠 What is DHCP?
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) it is a network management protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses to hosts. These hosts can be computers, printers,routers and servers. DHCP mainly uses port 67 for inbound and 68 for outbound connections. It has made life easier for the network adminstrators by dynamically assigning IP addresses, DNS servers, gateway addresses and subnet masks. You should also know that if you are getting an IP address from a DHCP server first it is assigned automatically and it can change over time because of a lease which is attached to the IP address which can last for a period of time.
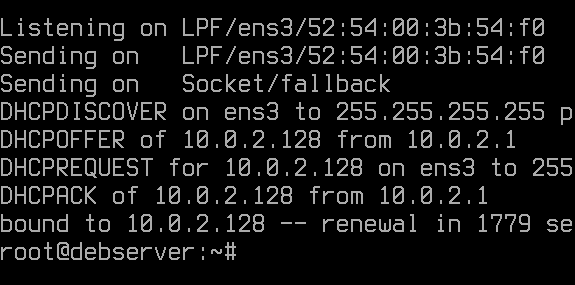
DHCP clients get their IP addresses from a DHCP server through the use of a four step process called DORA (Discovery Offering Request Acknowledgement). You can see the process from the image above.
⚙️ How DHCP Works – The DORA Process
Let us breakdown the DORA process using TCP/IP version 4 (or simply IPv4) as our example. In this scenario, our DHCP server will use the IP address 192.168.1.1.
🔍 1. Discovery
It is normal for computers to be configured to be able to obtain IP address automatically from a DHCP server. When a typical client on a network is first booted, it attempts to discover DHCP servers by sending a message to all recipients on the network at the same time. It does this to look for an IP address and also because it does not know the IP address of the DHCP server. Through the outbound port 68 the client tries to discover a DHCP server which in return the DHCP server listens for any requests using the inbound port 67. Once our client is able to discover the DHCP server in the network we move onto the next step Offering.
📦 2. Offering
When our DHCP server has been discovered by our client, in return it offers the client a gateway address, IP address, subnetmask and a DNS server IP address or more information it can give. The IP address that is offered to the client is usually selecte from a scope of IP addresses which are pre-configured by the Network Admin. For example if the Admin has configured the scope as a range of IP addresses spanning from 192.168.1.101-192.168.1.101 which is a range of 100 IP addresses this means the server can give out IP addresses to 100 clients in total before running out of IP addresses. After the DHCP server offers the client an IP address and additional info the next step is a Request from the client.
📨 3. Request
In most cases, especially if there is a single DHCP server, the client will “request” the IP address and additional TCP/IP information that has been offered by the DHCP server. That means that the client agrees to use the IP address, and it lets the server know this.
✅ 4. Acknowledgment
The server acknowledges that the client has requested the offered IP configuration. It then creates an IP lease for the client. The lease is available for a limited time, and that time is specified in the DHCP server configuration file. It could be as little as one hour (3600 seconds), or it could be 24 hours, or possibly 8 days.
It depends on the environment, organizational policies, type of system used, and administrator preferences. The lease information is written to a file on the server. That information typically includes the IP address the client will be using (in our example, 192.168.1.101), the client’s MAC address, the length of the lease, and possibly the hostname of the client. The server confirms with the client, and the client can now communicate over the network via TCP/IP. At this point, the server knows not to hand out the 192.168.1.101 IP address to any other clients. Instead, the next client that boots on the network will most likely receive the 192.168.1.102 IP address.
That is the 4-step DORA process. If you ever notice a system taking a few seconds to access a network it is probably because it is trying to obtain an IP address (and other TCP/IP-related information). Sometimes, this can take a few seconds or more. That will depend on the speed of your connection, the speed (and workload) of the DHCP server, and the amount of parameters that have to be written to the client.
I have learnt this by reading Dave Prowse book on building Linux servers, DHCP server and DNS servers. Here is a link to his course
I have no affliations with him. For more details, visit the official DHCP documentation.